Job Market Paper
1. Black by Popular Demand: Media Competition and the Evolution of Identity [Latest Draft]
What role do economic incentives play in social change? This paper examines this question through the lens of local newspaper markets during the U.S. Civil Rights era, following the emergence of the Black Power movement and the associated campaign to replace "Negro" with "Black." Combining text from Southern newspapers (1960–1973) and 1964 newspaper circulation audits, I show that the campaign constitutes a widespread and exogenous shock to media choice of label and narrative portrayal of Black individuals. Local market competition increased the elasticity of supply to ideological demand: accelerating label and narrative diffusion where audiences were receptive, but reinforcing inertia where they were resistant. These effects are not explained by editorial ideology or ownership. I then document that local markets exposed to earlier newspaper adoption of “Black” saw faster growth in Black local officeholding. The findings reveal how market incentives shape the diffusion of social and political movements.



Working Papers
2. Vertical Governance of Online Speech: Evidence from Google’s Moderation Mandate Latest Draft
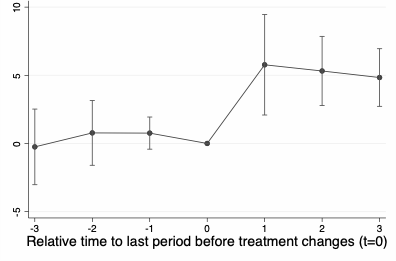
This paper shows that infrastructure providers can reshape online discourse by enforcing moderation through access-based leverage. Exploiting Google’s 2022 Play Store policy update in a triple-differences design across three alternative social media platforms, I find sharp and persistent declines in threatening content, especially among high-risk users. Politically sensitive narratives such as election denial also fell, highlighting how infrastructure-level enforcement can redefine the boundaries of online speech. I introduce a simple model of vertical governance to explain why distributors impose moderation requirements and why platforms choose either to comply or exit, clarifying the incentive trade-offs that underpin infrastructure-led enforcement.



3. The Political Effects of Threats to the Nation: Evidence from the Cuban Missile Crisis [New draft coming soon]
Joint with Tommaso Colussi
This project studies how citizens and political institutions respond to sudden, credible external threats. Using the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis as a natural experiment, and exploiting sharp geographic variation in perceived exposure to nuclear danger, we examine the crisis’s effects on electoral participation, partisan support, congressional behavior, and military service. Novel measures of local media exposure allow us to trace how threat salience translated into political and civic responses across U.S. communities.
4. From the Pulpit to the Polls: The Electoral Consequences of Christian Talk Radio
This paper studies the political effects of Christian-conservative radio expansion in the United States. Using variation in radio signal strength driven by topography and station acquisitions, I link exposure to county-level voting records and evangelical presence. Greater exposure increased Republican vote share, especially in areas with larger evangelical populations, highlighting how deregulation enabled partisan religious media to shape electoral outcomes.
5. Editorial Bias: Evidence from Historical Newspapers
This paper explores editorial bias showing systematic differences in language choices when newspapers published the same wire articles.
Climate
6. Climate on the Move: How Migration Imports Beliefs on Climate Change
(joint with Matteo Pograxha & Enrico Cavallotti)
This paper examines how climate shock-induced migration shapes the diffusion of climate change beliefs across international borders.
7. Selective Science: How Media Bias Shapes Climate Change Narratives
(joint with Matteo Pograxha)
This paper examines whether newspapers selectively cover climate science in ways that align with their audiences’ political priors, independent of article quality, shedding light on how media shape public perceptions of climate change.
AI
8. The Introduction and Reduction of Estimation Bias in AI Assisted Research
This paper explores how biases can affect LLM-assisted research and shows how methodological design can improve the reliability of AI-based textual analysis in the social sciences.
Development
9. When to baseline - The impact of lottery allocation household outcomes in a highly vulnerable setting
(joint with C. M. Fernandez, A. Guariso, M. Holmlund, T. Mitchell, and C. Newman.)
This paper examines whether public lottery allocation in field experiments affects survey outcomes, using evidence from villages in Niger.
